 |
|
Boltsman's constant.
The Basic equations of molecular-kinetic theory of Gases.
The Kinetic theory gases of an equation is given as The Kinetic energy of the gas = (12) mv2 Where m is the mass of the gas molecule and v is the velocity of the gas. The kinetic energy of the gas is also given by the equationKinetic energy of the gas = (32) kT Where k is the Boltzmann constant and T is the temperature in K
Temperature.
All molecules of a gas do not possess the same speed, and this could be explained by the fact that during the collision of molecules, the speed or momentum changes. If initially the speed of a molecule is the same, it changes after the molecular collision.
So it is seen that particles have different speeds, which are changing constantly. But although individual speed changes, the distribution of speed remains constant. That is the total velocity that does not change. But if the temperature of a gas is increased, then the average kinetic energy also changes.
Dependence of pressure on the molecules concentration and temperature.
Dependence on temperature and pressure
The Maxwell relation
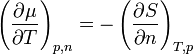
shows that the temperature variation of chemical potential depends on entropy. If entropy increases as the particle number increases, then chemical potential will decrease.
Similarly

shows that the pressure coefficient depends on volume. If volume increases with particle number, chemical potential also increases.
Boltsman's constant.
The Boltzmann constant (k or kB) is a physical constant relating energy at the individual particle level with temperature, which must necessarily be observed at the collective or bulk level. It is the gas constant R divided by the Avogadro constant NA:

It has the same dimension (energy divided by temperature) as entropy. It is named after the Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann.