 |
|
Chromosomes spread in the cytoplasm.
| P.O.C. | Phylum Schizophyta | Phylum Cyanophyta |
| Organism | 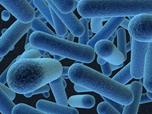 (Bacteria) (Bacteria)
|  (Blue-green algae) (Blue-green algae)
|
| Description | Spherical Rod-shaped Spiral | Unicellular organisms that contain different pigments |
| Feeding | Parasites Saprophytes | Autotrophic that photosynthesize their food. |
| Example | Tuberculosis bacteria | Nostoc |
| Benefits | Cheese – yogurt – vinegar industry | Produce food and oxygen |
| Harms | Parasitic bacteria cause diseases such as cholera , eye diseases , tuberculosis and diphtheria |
Kingdom Protista
General characteristics :
1. More developed than Monera
2. The chromosomes are found in the form of threads.
3. The nucleus is surrounded by nuclear membrane and contain nucleolus.
4. Cytoplasm may contain plastids.
| P.O.C. | Phylum Euglenophyta | Phylum Chrysophyta | Phylum Protozoa |
| Environment | Fresh water ponds and stagnant water | Marine and in fresh water | Fresh and salty water |
| Feeding | Autotrophic because they contain green plastids. | Autotrophic | Most are parasite on plants and animals |
| Examples | 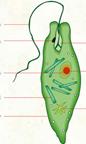 Euglena Euglena
|  Diatoms Diatoms
|  Paramecium Paramecium
|
| Benefits | Fish food, petroleum sediments | 
|
The cytoplasm of protozoa is divided into ectoplasm & endoplasm . Protozoa reproduce asexually & sexually.
Phylum Protozoa is subdivided into 4 classes:
| P.O.C. | Class sarcodina | Class Flagellata | Class ciliata | Class Sporozoa |
| Examples | Amoeba, Entamoeba | Trypanosoma | paramecium | plasmodium |
| Movement | pseudopodia | flagellum | cilia | |
| Diseases | dysentery | sleeping disease | Malaria | |
| Means of infection | Tsetse fly | mosquito |
Kingdom Fungi
General characteristics:
1. Some are unicellular and some are multicellular forming mycelium.
2. They have no chlorophyll txherefore they are parasites or saprophytes (get food from dead matter).
3. Some are useful (mushroom) and some are harmful (black rust)
| P.O.C. | PhylumZygomycetes | Phylum Ascomycetes | PhylumBasidomycetes |
| Examples |  Rhizopus (bread mould) Rhizopus (bread mould)
|  Saccharomyces Penicillium Saccharomyces Penicillium
|  Agaricus (Mushroom) Agaricus (Mushroom)
|
| Benefit | produce cortisone | Production of antibiotics (penicillin) Production of ethyl alcohol .
 Baking industry & flavoring Roquefort cheese. Baking industry & flavoring Roquefort cheese.
| Most species are edible as they are rich in protein , others are poisonous. |
Kingdom Plantae
| P.O.C. | Phylum Rhodophyta | Ph. Phaeophyta | Ph. Chlorophyta | Ph. Bryophyta |
Red Algae

| Brown Algae

| Green Algae

| ||
| Pigment | Red or pink | Brown | Green | |
| Structure | Simple or branched filaments | Simple or branched filaments | Unicellular or Multicellular | Terrestrial, unbranched filaments) |
| Example | Polysiphonia | Fucus Sargassum | Chlamydomonas Spirogyra | Riccia Funaria |
| P.O.C | Fungi | Algae |
| Examples | Bread mould, yeast, mushroom | Fucus, sargassum, spirogyra |
| Classification | Neither plants nor animals | primitive plants |
| Feeding | Heterotrophic . Some are saprophytes others are parasites. | Contain chlorophyll & are autotrophes |
 Phylum Tracheophyta
Phylum Tracheophyta


(ferns)
| Filicate (ferns) | Gymnosperms | |
| Description | Seedless , vascular plants which don't form flowers. | The reproductive organs are cones. Their seeds are naked. |
| Examples | Adiantum& Vougheir | Pines |
Angiosperms
| Subclass: Monocotyledon | Subclass: Dicotyledon | |
| Examples | Wheat, maize, palm, onion & cactus | Peas, cotton, roses |
| Roots | Fibrous root | Tap roots |
| Leaves | Parallel veined | Pinnate or palmate |
| Flowers | Trimerous or their multiplate | Tetramerous or pentamerous |
| Seeds |  One cotyledon One cotyledon
|  Two cotyledons Two cotyledons
|
| P.O.C | Gymnosperms | Angiosperms

|
| Examples | Pines | Palm , bean, roses |
 Reproductive organs Reproductive organs
| Cones | Flower (carpel , anther) |
| Seeds | Naked seeds | Covered seeds |
 |
Kingdom Animalia
| Phylum | Class | Order |
| 1. Porifera | ||
| 2. Colenterata | ||
| 3. Platyhelminthes | ||
| 4.Nematohelminthes | ||
| 5. Annelida | ||
| 6. Arthropoda | Crustacea, Archanida, Insecta, Myriopoda | |
| 7. Mollusca | ||
| 8. Echinodermata | ||
| 9. Chordata | Chondichthyes,
Osteichthyes
Amphibia
Reptilia
Aves
 Mammalia Mammalia
| Edentata Insectivora Carnivora Cetacea Ungulata Rodenta Chiroptera Lagomorpha Primates |
Kingdom Animalia
| Phylum | Porefera | Colenterata |
| Examples |  Sponges Sponges
| 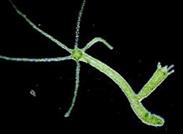 Hydra,
jelly fish,
corals Hydra,
jelly fish,
corals
|
| Environment | Aquatic animals which attach themselves to the base of rocks. | Aquatic animals
which attach
themselves to
 the base of rocks. the base of rocks.
|
| Description | The body wall has many lateral pores & canals. Skeleton of calcareous, siliceous spicules, fibers. |  Have stinging cells. Have stinging cells.
|
| Reproduction | Asexually (by budding) | |
| Sexually (by fusion of gametes) |
Kingdom Animalia